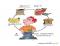
Irrigating a Colostomy
Content
Irrigating a Colostomy EQUIPMENTS Reservoir for irrigating fluids; irrigator bag or enema bag if irrigator bag not available Irrigating fluid: 500-1,500 mL lukewarm water or other solution prescribed by health care provider (Volume is titrated based on patient tolerance and results; average amount is 1,000 mL.) Irrigating tip: Cone tip or soft rubber catheter #22 or #24 with shield to prevent backflow of irrigating solution (Use only if cone not available) The cone is the preferred method to avoid possibility of bowel perforation.)Irrigation sleeve (long, largecapacity bag with opening at top to insert cone or catheter into stoma); available in different styles: Snap-on, self-adhering to skin, or held in place by belt Large tail closure Water-soluble lubricant. PROCEDURE: Nursing Action Preparatory phase 1.Explain the details of the procedure to the patient and answer any questions. Relieves anxiety and promotes compliance. 2. Select a consistent time, free from distractions. If the patient is learning to irrigate for bowel control, choose the time of day that will best fit into the patient's lifestyle. Establishes regularity. 3.Have the patient sit in front of the commode on chair or on the commode itself, providing privacy, and comfort. 4.Hang irrigating reservoir with prescribed solution so the bottom of the reservoir is approximately at the level of the patient's shoulder and above the stoma. Note: Colostomy irrigation may also be performed to empty the colon of its contents(feces, gas, mucus) before a diagnostic procedure or surgery and to cleanse the colon after fecal impaction removal or with constipation. Height of irrigation bag regulates pressure of irrigant. Performance phase 1. Remove pouch or covering from stoma, and apply irrigation sleeve, directing the open tail Allows water and feces to flow directly into commode. 2. Open tubing clamp on the irrigating reservoir to release a small amount of solution into the commode
Removes air from the setup; avoids air from being introduced into the colon, which can cause crampy pain. 3. Lubricate the tip of the cone/catheter, and gently insert into the stoma. Insert catheter no more than 3 inches (7.5 cm). Hold cone/shield gently, but firmly, against stoma to prevent backflow of water. Prevents intestinal perforation and irritation of mucous membranes. 4. If catheter does not advance easily, allow water to flow slowly while advancing catheter. NEVER FORCE CATHETER. Dilating the stoma with lubricated, gloved pinky finger may be necessary to direct cone/catheter properly. Slow rate relaxes bowel to facilitate passage of catheter. 5. Allow water to enter colon slowly over a 5- to10-minute period. If cramping occurs, slow flow rate or clamp tubing to allow cramping to subside. If cramping does not subside, remove cone/catheter to release contents. Cramping may occur from too rapid flow, cold water, excess solution, or colon ready to function. 6. Hold cone/shield in place 10 seconds after water is instilled, then gently remove cone/catheter from stoma.6.Discourages premature evacuation of fluid. 7. As feces and water flow down sleeve, periodically rinse sleeve with water. Allow 10-15 minutes for most of the returns, then dry sleeve tail and apply tail closure. 8. Leave sleeve in place for approximately 20more minutes while patient gets up and moves around. Ambulation stimulates peristalsis and completion of irrigation return. 9. When returns are complete, clean stomal area with mild soap and water; pat dry; reapply pouch or covering over stoma. Cleanliness and dryness promote comfort. Follow-up phase 1. Clean equipment with soap and water; dry and store in well-ventilated area. This will control odor and mildew, prolonging the life of equipment. 2. If applicable, the patient should use a pouch until the colostomy is sufficiently controlled It may take several months to establish control. The patient can then use mini pouch, stoma cap, or gauze covering as desired.
Removes air from the setup; avoids air from being introduced into the colon, which can cause crampy pain. 3. Lubricate the tip of the cone/catheter, and gently insert into the stoma. Insert catheter no more than 3 inches (7.5 cm). Hold cone/shield gently, but firmly, against stoma to prevent backflow of water. Prevents intestinal perforation and irritation of mucous membranes. 4. If catheter does not advance easily, allow water to flow slowly while advancing catheter. NEVER FORCE CATHETER. Dilating the stoma with lubricated, gloved pinky finger may be necessary to direct cone/catheter properly. Slow rate relaxes bowel to facilitate passage of catheter. 5. Allow water to enter colon slowly over a 5- to10-minute period. If cramping occurs, slow flow rate or clamp tubing to allow cramping to subside. If cramping does not subside, remove cone/catheter to release contents. Cramping may occur from too rapid flow, cold water, excess solution, or colon ready to function. 6. Hold cone/shield in place 10 seconds after water is instilled, then gently remove cone/catheter from stoma.6.Discourages premature evacuation of fluid. 7. As feces and water flow down sleeve, periodically rinse sleeve with water. Allow 10-15 minutes for most of the returns, then dry sleeve tail and apply tail closure. 8. Leave sleeve in place for approximately 20more minutes while patient gets up and moves around. Ambulation stimulates peristalsis and completion of irrigation return. 9. When returns are complete, clean stomal area with mild soap and water; pat dry; reapply pouch or covering over stoma. Cleanliness and dryness promote comfort. Follow-up phase 1. Clean equipment with soap and water; dry and store in well-ventilated area. This will control odor and mildew, prolonging the life of equipment. 2. If applicable, the patient should use a pouch until the colostomy is sufficiently controlled It may take several months to establish control. The patient can then use mini pouch, stoma cap, or gauze covering as desired.